Companies and Governments are Struggling with Cybersecurity
Report #1 Recap
In Sophic Capital’s Digital Defense report, we highlighted how susceptible people and organizations are to cybercrime. Despite the power of the internet, data, and technology, cybercrime losses reached a staggering US$12 billion in 2023. Organizations need to invest in cybersecurity to protect themselves and their clients. In this report, we look at the market size for cybersecurity and the trends that we believe make this a top investment theme in 2024 and beyond.
Business is Booming
(for both cybercriminals & cybersecurity companies)
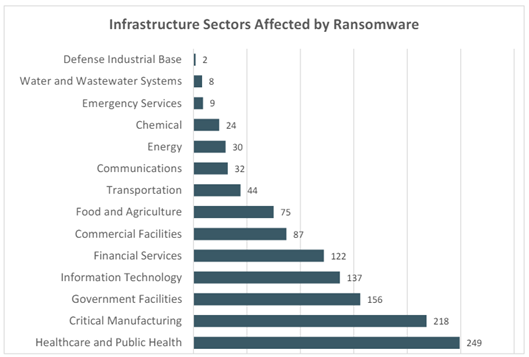
Cybercriminals steal your data, money, and assets. In today’s interconnected world, cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in IT systems, catching organizations off-guard and compromising their data and finances. As the digital economy expands, so does the scale and sophistication of digital crime. At the current trajectory, the annual cost of cyberattacks is projected to reach US$10.5 trillion annually by 2025. These attacks are becoming more strategic, impacting critical infrastructure and economic cornerstones. Exhibit 1 shows the critical infrastructure entities that were impacted by ransomware attacks in 2023, which is up 37% year-over-year.
Exhibit 1: Infrastructure Sectors Affected by Ransomware Attacks in 2023
The cybersecurity industry encompasses a wide range of products, services, and solutions designed to protect digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and data breaches. As enterprises increasingly digitize their operations, the sophistication and frequency of cyber threats have escalated, making cybersecurity a critical concern across all industries.
Cybersecurity is a big problem with potential market values of:
- US$190 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to reach $US298.5 billion in 2028, a 9.4% CAGR% (MarketsandMarkets).
- US$173 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to reach $US425billion in 2030, a 13.8% CAGR (Fortune Business Insights).
- US$179.8 billion in 2022 and is forecasted to reach $US408.6 billion in 2032, an 8.6% CAGR (DataHorizzon Research).
Cybersecurity Industry Challenges and Opportunities
Technological Advancements and Threat Evolution. The cybersecurity market is dynamic, evolving rapidly in response to the ever-changing threat landscape and technological advancements. Businesses are investing heavily in cybersecurity to safeguard their assets and mitigate risks.
Point Technologies versus Integration Challenges. Vendors are introducing point technologies to address specific security pain points. While these solutions offer targeted benefits, they often lack seamless integration with existing systems, leading to management complexities and potential security gaps. Ironically, consolidation and integration efforts can also contribute to technological sprawl and buyer confusion.
Customer Demands and Technological Constraints. Commercial solutions currently available do not fully meet customer demands in terms of automation, pricing, and services. Organizations typically adopt technological changes incrementally due to legacy investments and budget limitations. A complete shift from traditional firewalls to zero trust access control is unlikely overnight.
The Gap Between Vended Market and Addressable Market. Exhibit 2 highlights a significant gap between the existing cybersecurity market and its full addressable potential. Bridging this gap requires providers and investors to better serve underserved segments, enhance technology, and reduce complexity.
Unique Moment for Innovation. The current buyer climate presents an opportunity for innovation within the cybersecurity industry. As cyber threats continue to escalate and regulatory pressures mount, organizations must adapt to the ongoing digitization of the global economy.
Exhibit 2: Global Cybersecurity Total Addressable Market, as per McKinsey & Company
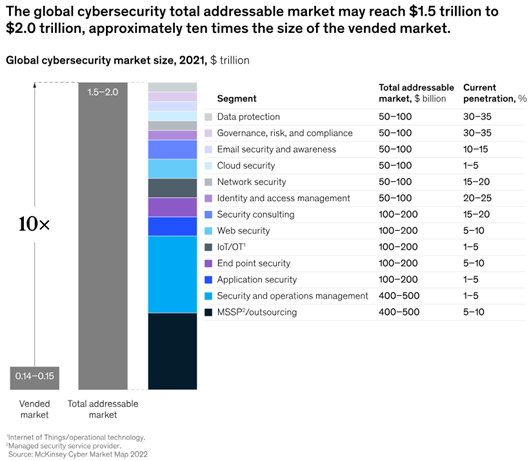
The under-penetration of cybersecurity products and services stems from organizations’ below-target adoption which leaves them vulnerable against new and developing threats. To address this challenge, cybersecurity providers must modernize their capabilities and rethink go-to-market strategies. To capitalize on opportunities, providers should focus on:
- Cloud Technologies: Leveraging cloud-based solutions for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Pricing Mechanisms: Offering transparent, value-based pricing models that resonate with customers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Harnessing AI for threat detection, incident response, and automation.
- Managed Services: Particularly in the midmarket, providing comprehensive security services.
As various cybersecurity companies adapt their products to keep up with technological advancements, the current cybersecurity market becomes increasingly fragmented. By strategically addressing these areas, cybersecurity providers can enhance competitiveness and cut their own piece out of the US$2 trillion pie.
Safety From Above
The widespread adoption of cloud technology, the normalization of hybrid workforces, the rise of generative AI, along with established regulatory requirements that continue to evolve are compelling security and risk management leaders to increase their spending. In 2024, global end-user spending on security and risk management is projected to reach US$215 billion, representing a 14.3% increase from 2023.
Approximately 82% of data breaches involve data stored in the cloud, whether public, private, or across multiple environments. These breaches result from evolving ransomware attacks, cloud misconfigurations, and exploitation of vendor systems. Large companies aren’t the only victims. Smaller organizations, experiencing rapid growth, face heightened risks due to their expanding digital touchpoints and ecosystem relationships.
For instance, mid-sized firms often serve as suppliers or partners within global supply chains. Cyber attackers exploit these connections, using smaller companies as entry points to infiltrate larger networks. The interconnected nature of modern supply chains means that a breach in one company can have cascading effects, affecting multiple entities.

AI in Cybersecurity
In the foreseeable future, AI will be pivotal in cybersecurity, revolutionizing threat detection, incident response, and predictive intelligence. As AI algorithms evolve, they will enhance security by automating tasks, identifying intricate threats, and bolstering overall resilience against cyberattacks. Dimension Market Research estimates that the global AI in cybersecurity market was valued at US$22.1 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to reach $US147.5 billion in 2033, growing at a CAGR of 20.8%
As online security threats escalate, demand for advanced solutions is skyrocketing. Outdated network security solutions fall short in safeguarding enterprises against sophisticated network, cloud, and endpoint security threats. The dynamic landscape calls for innovative approaches to stay ahead of cyber adversaries.
Security-as-a-Service (SECaaS)
How can SMEs acquire security solutions to secure industrial operations against severe cyber attacks? Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often encounter obstacles when adopting security solutions due to implementation costs and the need for regular updates. Compounding this is a shortage of skilled professionals in security solution development.
Managed cybersecurity services offer an appealing solution for SMEs. Despite staffing limitations and budget constraints, these services enhance security effectively. The global Security-as-a-Service (SECaaS) market was valued at US$12.4 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach US$23.8 billion by 2026, a CAGR of 13.8%. The shift toward managed services addresses the challenges faced by SMEs in maintaining robust security measures.
SMEs are increasingly adopting cloud-based security services due to their cost-effectiveness and risk reduction benefits. Regulatory and compliance pressures are also driving organizations to seek managed security solutions for operational efficiency. SECaaS allows flexible scaling, enabling SMEs to deploy security measures as required. As a subscriber to a cloud service, SMEs can select the subscription tier that aligns with their needs, avoiding unnecessary spending. Having access to security experts with the latest tools and updates provides faster provisioning and simpler management, ultimately freeing up resources so enterprises can focus on running their businesses.
Strong Tailwinds Propelling Cybersecurity Outlook
International Conflict Accelerates Cybersecurity Investment
As the global digital transformation accelerates, hackers now have unprecedented access to sensitive data. This situation can lead to conflicts not only between individuals, organizations, and cybercriminals seeking profit but also nations at the geopolitical level. Given the global nature of modern cyber warfare, nations must adopt universally coordinated and revamped tactics to effectively combat sophisticated adversaries in the digital battlefield.
Ukraine and Palestine have become battlegrounds for both cyber and kinetic attacks, with all parties employing highly sophisticated techniques to target military and governmental systems. These conflicts have significantly impacted the cybersecurity industry, leading to increased demand for cybersecurity services and products. The driving force behind this demand is the increased government expenditure on cybersecurity measures in response to the wars.
Furthermore, war has accelerated the development of cybersecurity technologies, particularly in the fields of AI and machine learning. These innovative technologies are now widely used for identifying and neutralizing cyber threats.
Countries do not have to be at war to receive attacks from foreign entities. The United States and United Kingdom have both accused China of conducting cyberattacks on individuals as well as organizations.

Regulatory Changes Drive Strategic Shifts and Budget Increases
In the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, protecting sensitive data and critical systems has become more urgent than ever. Regulatory actions have intensified due to significant developments like the SEC’s rules on cybersecurity incident disclosure and the EU’s Cyber Resilience Act (CRA). Simultaneously, the race to harness AI is heating up, prompting calls for responsible use, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
The SEC’s new rules require public companies to disclose significant cyber incidents within four business days and detail their boards’ oversight of cybersecurity risks. This has driven investment in prevention to avoid such incidents. However, cyber insurance has become harder to obtain and maintain, making it more expensive for companies to comply with regulations. Boards now face the choice of significantly increasing cybersecurity spending or risk being uninsurable from a cyber perspective.
SMEs also feel the pressure of increasing data protection regulations like the GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. Unlike larger corporations, SMEs often lack dedicated compliance teams and resources to navigate these complex rules effectively. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal consequences, but maintaining compliance without robust cybersecurity measures is challenging. Attackers exploit this vulnerability by demanding ransoms while holding SMEs’ data hostage.
As AI becomes integral to cybersecurity, regulation becomes crucial. Colorado’s new AI law mandates that developers of high-risk AI systems avoid algorithmic discrimination and disclose system information, highlighting the growing regulatory landscape. Ensuring AI-powered tools strengthen defenses without introducing vulnerabilities requires a strategic and vigilant approach.
A survey conducted by Swimlane and Sapio Research revealed that 93% of organizations have reevaluated their cybersecurity strategies in response to new regulations, with 58% completely reconsidering their approach. Consequently, cybersecurity budgets have significantly increased, with 92% of organizations allocating more resources.
Continued Skill Shortage Increases Value of Solutions
The cybersecurity industry is grappling with a critical shortage of skilled professionals. The global cybersecurity workforce expanded by 12.6% between 2022 and 2023, but the talent gap persists. The World Economic Forum declared that the global cybersecurity industry urgently needs four million professionals. By 2030, estimates suggest a global talent shortage exceeding 85 million workers, potentially resulting in $8.5 trillion in unrealized annual revenue.
In the United States, there are over 700,000 vacant positions in the cybersecurity field. These opportunities extend beyond technical roles and encompass areas such as ethical hacking, legal expertise, and the rapidly expanding cyber insurance sector.
Information security jobs are projected to grow by 32% between 2022 and 2032. Organizations, especially large enterprises, struggle to attract and retain cybersecurity talent. Older corporate cultures and lack of equity participation hinder their efforts. Therefore, service providers offering specialized cybersecurity expertise become crucial partners for bridging the talent gap.
There was a 72% climb in the number of data breaches worldwide in 2023. AI adoption compounds the challenge. Organizations must balance data privacy, integrate AI solutions, and address model vulnerabilities. Experienced human oversight remains essential, given the scarcity of skilled cybersecurity professionals.
The global cybersecurity talent shortage presents both risks and opportunities. Consolidation within the market drives vendors to integrate standalone tools into comprehensive platforms. However, the shortage of skilled labor complicates deployment and operation, favoring solutions providers over traditional vendors. Investing in the right players can yield substantial returns while contributing to a safer digital landscape
Conclusion
Cybercriminals employ diverse tactics to disrupt companies, ranging from malware-infected systems erasing critical data to malicious code restricting website access. The rapid digital transformation and heightened awareness of cyber risks are key drivers behind the cybersecurity market’s growth. However, a shortage of skilled professionals necessitates innovative solutions.
The disruptive tactics implored by cybercriminals impact business continuity, data integrity, and customer trust. Organizations’ increasing reliance on digital technologies fuels the demand for robust cybersecurity solutions. Heightened awareness of cyber risks drives investment in protective measures. As companies adopt cloud services and AI, their vulnerability to cyberattacks grows.
Multinationals must adapt to evolving compliance landscapes. Traditional single-tenant applications face compliance demands and business risks while nationalistic privacy regulations and data localization requirements fragment enterprise architectures. Beyond national security, cybersecurity is a critical risk-mitigation pillar for companies. As skilled professionals are scarce, this emphasizes the need for innovative solutions.
As digital landscapes shift, cybersecurity remains pivotal. Investors should closely monitor companies providing effective solutions contributing to a safer digital environment.
Coming Up…
In our next report, we’ll introduce Sophic Capital client Plurilock Security Inc. [TSXV:PLUR, OTC:PLCKF], a cybersecurity solutions provider for the United States and Canadian Federal Governments along with Global 2000 companies. Through these relationships, Plurilock sells its unique brand of Critical Services, aiding clients with expertise to defend against, detect, and prevent costly data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Disclaimers
The information and recommendations made available through our emails, newsletters, website and press releases (collectively referred to as the “Material”) by Sophic Capital Inc. (“Sophic” or “Company”) is for informational purposes only and shall not be used or construed as an offer to sell or be used as a solicitation of an offer to buy any services or securities. In accessing or consuming the Materials, you hereby acknowledge that any reliance upon any Materials shall be at your sole risk. None of the information provided in our monthly newsletter and emails or any other Material should be viewed as an invite, and/or induce or encourage any person to make any kind of investment decision. The recommendations and information provided in our Material are not tailored to the needs of particular persons and may not be appropriate for you depending on your financial position or investment goals or needs. You should apply your own judgment in making any use of the information provided in the Company’s Material, especially as the basis for any investment decisions. Securities or other investments referred to in the Materials may not be suitable for you and you should not make any kind of investment decision in relation to them without first obtaining independent investment advice from a qualified and registered investment advisor. You further agree that neither Sophic, its, directors, officers, shareholders, employees, affiliates consultants, and/or clients will be liable for any losses or liabilities that may be occasioned as a result of the information provided in any of the Material. By accessing Sophic’s website and signing up to receive the Company’s monthly newsletter or any other Material, you accept and agree to be bound by and comply with the terms and conditions set out herein. If you do not accept and agree to the terms, you should not use the Company’s website or accept the terms and conditions associated to the newsletter signup. Sophic is not registered as an adviser or dealer under the securities legislation of any jurisdiction of Canada or elsewhere and provides Material on behalf of its clients pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirements that is available in respect of generic advice. In no event will Sophic be responsible or liable to you or any other party for any damages of any kind arising out of or relating to the use of, misuse of and/or inability to use the Company’s website or Material. The information is directed only at persons resident in Canada. The Company’s Material or the information provided in the Material shall not in any form constitute as an offer or solicitation to anyone in the United States of America or any jurisdiction where such offer or solicitation is not authorized or to any person to whom it is unlawful to make such a solicitation. If you choose to access Sophic’s website and/or have signed up to receive the Company’s monthly newsletter or any other Material, you acknowledge that the information in the Material is intended for use by persons resident in Canada only. Sophic is not an investment advisor, nor does it maintain any registrations as such, and Material provided by Sophic shall not be used to make investment decisions. Information provided in the Company’s Material is often opinionated and should be considered for information purposes only. No stock exchange or securities regulatory authority anywhere has approved or disapproved of the information contained herein. There is no express or implied solicitation to buy or sell securities. Sophic and/or its principals and employees may have positions in the stocks mentioned in the Company’s Material and may trade in the stocks mentioned in the Material. Do not consider buying or selling any stock without conducting your own due diligence and/or without obtaining independent investment advice from a qualified and registered investment advisor. The Company has not independently verified any of the data from third party sources referred to in the Material, including information provided by Sophic clients that are the subject of the report, or ascertained the underlying assumptions relied upon by such sources. The Company does not assume any responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of this information or for any failure by any such other persons to disclose events which may have occurred or may affect the significance or accuracy of any such information.
The Material may contain forward looking information. Forward-looking statements are frequently, but not always, identified by words such as “expects,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “intends,” “estimates,” “potential,” “possible,” “projects,” “plans,” and similar expressions, or statements that events, conditions or results “will,” “may,” “could,” or “should” occur or be achieved or their negatives or other comparable words and include, without limitation, statements regarding, projected revenue, income or earnings or other results of operations, strategy, plans, objectives, goals and targets, plans to increase market share or with respect to anticipated performance compared to competitors, product development and adoption by potential customers. These statements relate to future events and future performance. Forward-looking statements are based on opinions and assumptions as of the date made and are subject to a variety of risks and other factors that could cause actual events/results to differ materially from these forward-looking statements. There can be no assurance that such expectations will prove to be correct; these statements are no guarantee of future performance and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors. Sophic provides no assurance as to future results, performance, or achievements and no representations are made that actual results achieved will be as indicated in the forward-looking information. Nothing herein can be assumed or predicted, and you are strongly encouraged to learn more and seek independent advice before relying on any information presented.


