Real Results from Virtual Meetings
Problem: New Technologies Needed to Facilitate Engaging Interactions
Event organizers are witnessing the revival of in-person events, with increasing attendance on trade show floors and at annual conferences. Simultaneously, as businesses are grappling with skyrocketing costs of in-person interactions, they are embracing technology-driven solutions as a result of lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, companies are reimagining how in-person events are held, which until recently had remained largely unchanged for decades. However, spatial computing, the technology that was originally referred to as the metaverse, is emerging as a potential solution that businesses can leverage to meet their in-person event needs. Many investors had previously written off the metaverse, as they did not understand meaningful end-user applications. The technology is now re-merging as a collection of solutions and tools with virtual business interactions being a key application.
Current Solution: In-Person Events and Meetings Are Inadequate
In-person events can now be exorbitantly expensive, are often inconvenient and unengaging. Looking at the average customer journey: attendees are confronted with high costs, inconvenient travel experiences, and crowded/unengaging conferences, which are difficult to navigate. These factors lead to attendees having less than the most productive interactions, despite paying high costs to attend these events. Most attendees likely only meet a few people, maybe get a warm lead or two, but the cost-benefit of making the journey to the conference seems lopsided. Now imagine if you were the one trying to organize a multi-day event for 1,000+ people.
While there is nothing quite like meeting someone in-person, getting that firm handshake, making your first impression, COVID-19 showed us the power of remote work, especially when it comes to interacting with existing connections. Powerful video conferencing platforms are enabling rich virtual experiences, improving productivity, and driving demand for remote access to events and meetings.
Recent Spatial Computing Advances Could Improve In-Person Interactions In A Business Setting
“Spatial computing”, can help foster interactions, increasing engagement without massively growing costs.One definition of “spatial computing” that we like is the next iteration of the Internet, where it becomes something we are immersed in, rather than something we just view. We like to think of spatial computing, or as some people call it, the metaverse, as a new gateway to digital experiences, a way to deepen connectivity and complement everyday activities.
Another way we like to think about spatial computing is as a platform that transcends physical boundaries, enabling users to virtually connect with others regardless of geographical location. It offers an immersive and interactive experience that goes beyond traditional social media platforms, revolutionizing online social interactions and providing a wide array of additional benefits. Spatial computing enhances online learning, education, and gaming while offering promising prospects for transforming the working environment.

Spatial computing technology has seen rapid advances and could be a potentially transformative solution to facilitate more engaging interactions in business settings. Early adopters and companies are already experiencing real-life advantages, as a result. In 2021, venture capital and private-equity funding for spatial computing amounted to US$13 billion. Within the first five months of 2022 alone, worldwide investments in the metaverse space exceeded US$120 billion, more than double the US$57 billion invested in the entire year of 2021. In 2022, the market size for the metaverse reached a value of US$62 billion. Emergen Research expects the market to expand from US$62 billion in 2022 to US$1.3 trillion by 2030, demonstrating a CAGR of 47.2% throughout the forecast period.
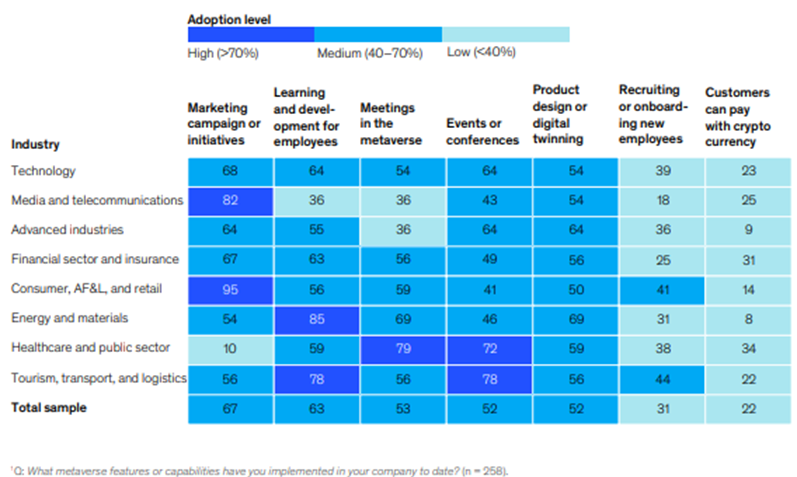
Spatial computing is poised to become the primary growth frontier for numerous industries in the next ten years. This is primarily due to its extensive range of potential applications and uses, as well as the substantial investments made by major technology companies, venture capital firms, corporations, and brands. The top five spatial computing use cases for enterprises are (Exhibit 1):
-
- Implementing marketing campaign or initiatives
- Learning and development for employees
- Meetings
- Events or conferences
- Product design or digital twinning
Exhibit 1: Spatial Computing Initiatives Implemented to Date, by Industry (1), % of senior executives in each industry
Among the two-thirds of consumers who have tried spatial computing, 80% of them value the shared virtual experience with their peers. A significant 59% of consumers expressed enthusiasm about transitioning their daily activities to spatial computing. And among companies that are aware of spatial computing, 57% state that they are actively adopting it. Additionally, 63% prefer virtual work meetings over in-person ones, and 59% find virtual educational sessions more enjoyable than their physical counterparts. Moreover, the findings indicate that 62% of spatial computing users have actively participated in branded virtual experiences, highlighting a promising opportunity for companies to explore and invest in such initiatives. Gartner predicts 25% of people will spend at least one hour per day in the metaverse by 2026, and it is highly conceivable that by 2030, over half of all live events could potentially take place within the metaverse.
Virtual Events Expected to Quadruple By 2030 to US$1 Trillion Market
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a substantial increase in the demand for and use of virtual conferences and meetings, of various sizes and for different purposes since in person meetings were not feasible. A virtual event could refer to an event held within an immersive simulated online environment using spatial computing. But the term “virtual event” can be interpreted in several ways, typically referring to remote web-based gatherings that replicate the various elements found in physical events. While any company or organization can host such events, they share two common characteristics: 1) They take place exclusively in the virtual realm, devoid of physical presence; and 2) They provide interactive breakout sessions, vendor interactions, and networking opportunities akin to those offered by on-site events.
Virtual events come in various sizes, ranging from small-scale to large-scale, and can be either private or public. These events encompass a wide range of activities, including business meetings, conferences, concerts, and festivals. The popularity of virtual events is rising due to the distinct and immersive experiences they provide, often surpassing what is achievable in the physical realm.
Webinars emerged as the most favoured digital activity in 2020 according to event visitors in the exhibition industry, and are expected to play a prominent role going forward. The ON24 Webinar Benchmarks Report for 2021 further highlights the significance of webinars, with 72% of marketers acknowledging their direct impact on revenue and pipeline. Furthermore, another survey cited on Statista revealed that webinars are considered a crucial component of the marketing strategy for 99% of respondents from both small businesses and enterprises. The survey also found that webinars generate substantial leads, surpassing other channels, as reported by 89% of participants. Additionally, 78% of respondents stated that webinars contribute to a decrease in their cost per lead.
By 2032, the global market size for virtual events is projected to reach approximately US$1 trillion, with a CAGR of 18.8% from 2023 to 2032, according to Market.US. This growth would peg the virtual event industry growing nearly three times as fast as the overall events industry, according to industry data. Within that, the U.S. virtual events market size was valued at US$76 billion in 2022 and could reach an estimated US$409 billion by 2032. This growth can be attributed to the increasing preference for virtual events as a means of conducting day-to-day business activities, including video calls, live chats, video conferences, and online meetings, enabling real-time data sharing. COVID-19 and the subsequent lockdowns and movement restrictions have played a significant role in driving the market’s expansion with the need to facilitate remote work arrangements further contributing to the anticipated growth of this market. The event industry as whole is estimated to reach a value of US$2.1 trillion by 2032, up from US$1.1 trillion in 2019 growing at a CAGR of 6.4%, according to Allied Market Research. While this is still a large and growing market, industry data implies that a greater share of event economics will be captured by virtual events in the near future.
The convenience offered by virtual events has led to a significant rise in the popularity of hybrid events, which combine both in-person and virtual elements. Hybrid events essentially involve traditional physical gatherings supplemented with technology that enables virtual attendance for individuals unable to be physically present. Prior to the pandemic, hybrid or virtual events constituted only 18.9% of all events. However, following the pandemic there has been a notable shift, with 59.5% of event planners expressing their intention to incorporate hybrid events in their future plans.
Leveraging the Power of the Spatial Computing for Virtual Events
The advancement of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, along with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) applications, is shaping the future of event planning. Trade events have long served as a vital component of business-to-business (B2B) marketing, aiming to establish year-long communities and provide a 365-day, on-demand marketplace for lead generation. Additionally, there is a need for platforms that facilitate networking opportunities and grant access to educational resources for both buyers and sellers. The metaverse presents numerous opportunities in these areas, with the ability to collect unlimited data. While it may not replace physical events entirely, it has the potential to significantly enhance the event experience and sustain momentum.
Numerous prominent tech companies, including Meta (formerly Facebook) and Apple, have announced ambitious spatial computing plans and made heavy investments in the space. Initially met with skepticism, large technology companies are advancing spatial computing technologies, which will directly improve virtual events and business meetings. Apple launched the Vision Pro headset at a price of US$3,500, with plans underway for a more cost-effective model to increase accessibility. The upcoming iteration of Apple’s Vision Pro aims to be a more budget-friendly VR/AR headset, targeting a price point below US$2,500. In contrast, Meta intends to surpass Apple’s Vision Pro with an even more competitive pricing strategy and improved user-friendliness. Meta is looking ahead to a follow-up to the Quest 3, drawing inspiration from Apple’s Vision Pro while simultaneously striving to bring its VR technology into the mainstream. Meta has shifted its focus from a heavy emphasis on the metaverse to emphasizing the practical applications of the headset, including gaming and productivity.

As spatial computing is still in its early stages, it is essential to consider its potential positive impact on event experiences, including:
-
- Interactive 3D digital spaces that offer engaging experiences instead of merely streaming video presentations;
- Fully virtual events;
- Virtual tours of event venues, travel destinations, and opportunities in the hospitality and entertainment sectors;
- Enhanced brand engagement through interactive experiences;
- Immersive educational programs, including virtual workshops that supplement the presented material, and;
- Virtual show floors that enable attendees, without or without using VR goggles, to explore booths, collaborate, and connect with others without physically attending.
One such virtual event example is how the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) built a virtual replica of its iconic trading floor for initial public offering events. Developed as way for remote workforces to participate in events that were previously limited in attendance by room capacity, individuals across the world are now taking part in the ceremonial bell-ringing through a virtual replica of the iconic NYSE trading floor.
Spatial computing is set to bring about incremental enhancements to existing enterprise solutions, as well as introduce entirely new innovations. One major area of improvement will be enhanced remote collaboration: As online meetings in the metaverse evolve, we can anticipate a shift from 2D screens to immersive 3D spaces, enabling more effective remote work and potentially reducing the need for physical co-location. This transition is expected to align with the ongoing re-evaluation of organizational structures, which was prompted by the pandemic. A second major area of improvement will be rethinking learning and development: The metaverse will revolutionize the learning process by providing simulations of real-life settings and situations, leading to more engaging educational experiences.
Conclusion
Based on the data presented, it appears that virtual events, whether fully online or hybrid, are likely to become a permanent fixture for enterprises, and not just be a temporary COVID-19 driven work around. The convenience offered by virtual events makes it challenging for a digitally connected workforce to relinquish this technology, especially as in-person events see their costs soar. Despite the increasing number of individuals attending physical events, evidence suggests that a significant portion of workforces prefer the option to participate online. Furthermore, the technology surrounding hybrid events is rapidly advancing, promising an enhanced virtual event experience. “Xcyting” times lie ahead in the global market for virtual events, urging us to embrace these technological advancements and anticipate a more digitally oriented future.
Coming Up…
In our next report, we will introduce new Sophic Capital client Xcyte Digital Corp. [TSXV-XCYT] (expected to begin trading shortly on November 15th). Xcyte is a spatial computing event technology aggregator and developer providing a high value, cost effective, multi-platform subscription service to host virtual events with no VR headset required for participation. New solutions, such as those offered by Xcyte, leveraging new technologies now enable “Virtual Events”, which can bring the best of both in-person and virtual events to attendees.
For More Research
Access more Sophic Capital research HERE
Sign up for Sophic Capital’s reports HERE
Disclosures
Xcyte Digital Corp. [TSXV-XCYT] has contracted Sophic Capital for capital markets advisory and investor relations services.

